RoHS-Compliant Materials play a vital role in electronics manufacturing by ensuring products meet strict environmental standards. These materials contain reduced levels of hazardous substances, such as lead and cadmium, which can harm ecosystems and human health. The RoHS Directive has transformed the industry, encouraging cleaner practices and innovation. For example:
Electronic enclosures, often overlooked, are essential for product safety. They shield components and ensure compliance with RoHS regulations, protecting both users and the planet.
The RoHS Directive, short for "Restriction of Hazardous Substances," is a regulation that limits the use of specific hazardous materials in electrical and electronic equipment. It was first introduced in 2003 by the European Union to address environmental and health concerns caused by toxic substances in electronics. Over time, the directive has evolved to strengthen its impact.
| Year | Regulation/Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2011 | RoHS 2 Directive | Enhanced the original directive, requiring periodic re-evaluations. |
| 2013 | RoHS 2 Implementation | Expanded the scope to include more electronic and electrical equipment. |
| 50 years prior | Research in Toxicology | Highlighted the long-term effects of low-level chemical exposure. |
RoHS standards now serve as a global benchmark for reducing hazardous materials in electronics, ensuring safer products for consumers and the environment.
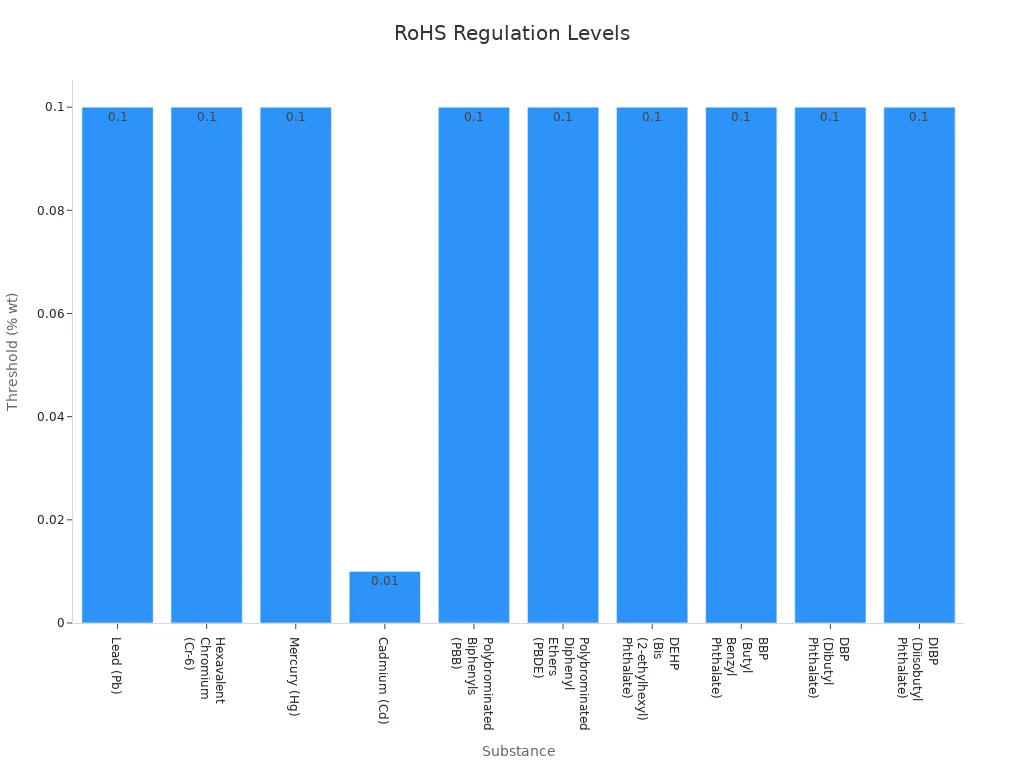
RoHS regulations restrict the use of ten hazardous substances in electronics. These substances, if not controlled, can harm ecosystems and human health. Below is a table listing the restricted substances and their maximum allowable concentrations:
| Substance | Maximum Concentration |
|---|---|
| Lead (Pb) | 0.1% by weight |
| Hexavalent Chromium (Cr-6) | 0.1% by weight |
| Mercury (Hg) | 0.1% by weight |
| Cadmium (Cd) | 0.01% by weight |
| Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBB) | 0.1% by weight |
| Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE) | 0.1% by weight |
| DEHP (Bis (2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate) | 0.1% by weight |
| BBP (Butyl Benzyl Phthalate) | 0.1% by weight |
| DBP (Dibutyl Phthalate) | 0.1% by weight |
| DIBP (Diisobutyl Phthalate) | 0.1% by weight |
These restrictions encourage manufacturers to adopt safer alternatives, reducing the environmental footprint of electronic products.
RoHS compliance plays a critical role in improving the safety and sustainability of electronics. For example:
Additionally, RoHS certification aligns manufacturers with international standards, especially for those targeting the European market. It also enhances customer trust and provides legal protection. By adhering to RoHS, you contribute to a safer and more sustainable future.
When selecting materials for electronic enclosures, you must prioritize those that meet RoHS standards. These materials ensure your products are safe, durable, and environmentally friendly. Commonly used RoHS-compliant materials include:
These materials comply with RoHS regulations, ensuring they contain minimal hazardous substances. For example, aluminum and stainless steel are naturally free of restricted substances like lead and cadmium. Plastics like PC and ABS are manufactured to meet RoHS standards by avoiding harmful additives.
RoHS-compliant materials offer several benefits that make them essential for electronic enclosures. Their properties ensure safety, durability, and environmental responsibility. Key advantages include:
| Directive | Year | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RoHS | 2002 | Limits on hazardous substances in electronic products. |
| RoHS 2 | 2011 | Marking and record-keeping requirements for compliance. |
| RoHS 3 | 2015 | Added four more restricted substances to the original list. |
By choosing RoHS-compliant materials, you not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance the quality and sustainability of your products.
Avoiding non-compliant materials is just as important as selecting the right ones. Materials that fail to meet RoHS standards can harm the environment and pose health risks. Common non-compliant materials include:
Using non-compliant materials can lead to regulatory penalties, product recalls, and damage to your brand reputation. Always verify the compliance of your materials through proper documentation and testing.
Sourcing materials that meet RoHS standards is a critical step in manufacturing compliant electronics. You need to establish a robust supply chain strategy to ensure all materials align with RoHS regulations. Start by communicating clearly with your suppliers about compliance requirements. This helps you avoid non-compliant materials that could jeopardize your product's certification.
To streamline sourcing, consider these strategies:
- Build procurement contracts that specify RoHS compliance for all materials.
- Develop a RoHS compliance program with clear steps for managing suppliers.
- Incorporate compliance checks into your standard business practices.
- Use management reports to make informed sourcing decisions and mitigate risks.
These practices not only help you source compliant materials but also build resilience and sustainability into your operations. By prioritizing RoHS-compliant materials, you reduce the risk of regulatory penalties and enhance your product's marketability.
Proper documentation and certification are essential for proving RoHS compliance. You must maintain detailed records of all materials and components used in your products. This documentation serves as evidence during inspections and audits, ensuring your products meet RoHS regulations.
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) oversees the technical aspects of RoHS compliance, while individual EU member states enforce the regulations. To ensure credibility, you should:
- Use accredited laboratories for testing components and final products.
- Obtain certificates of conformity for all materials under RoHS regulations.
- Document all test results and certifications for future reference.
For example, the SASO RoHS regulation requires a certificate of conformity evaluated by approved Notified Bodies. Additionally, manufacturers must comply with safety and environmental standards to obtain the Product Certification of Conformity (PcoC). These steps not only ensure compliance but also build trust with regulatory bodies and customers.
Quality control plays a vital role in maintaining RoHS compliance throughout the manufacturing process. Regular testing ensures that your materials and products meet the required standards. You should implement a rigorous quality control system that includes:
1. Testing raw materials for restricted substances before production.
2. Conducting periodic checks on finished products to verify compliance.
3. Using advanced testing methods, such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF), to detect hazardous substances.
Partnering with accredited laboratories for testing adds credibility to your compliance efforts. These labs use scientific methods to verify that your products meet RoHS regulations. By documenting all test results, you create a transparent record that demonstrates your commitment to compliance. This not only protects your business from penalties but also enhances your reputation in the market.
Using RoHS-compliant materials significantly reduces the environmental impact of electronics manufacturing. These materials limit hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can leach into soil and water, harming ecosystems. By choosing RoHS-compliant materials, you help prevent these toxic chemicals from entering the environment. This not only protects wildlife but also reduces the risk of contamination in food and water supplies.
From a health perspective, RoHS compliance minimizes exposure to harmful substances during production and disposal. Workers in manufacturing facilities face fewer risks when handling safer materials. Additionally, consumers benefit from products that are free from toxic chemicals, ensuring safer usage in homes and workplaces.
Adopting RoHS-compliant materials positions your business to meet global regulatory standards. This compliance is essential for accessing markets like the European Union, where RoHS regulations are strictly enforced. Without compliance, your products may face bans or restrictions, limiting your market reach.
The growing demand for RoHS-compliant products also drives market growth. For instance:
- The global RoHS Testing Equipment market was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 2.3 billion by 2032.
- This market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.1%, reflecting the increasing need for compliance testing.
- Rising awareness about e-waste hazards has further boosted the demand for RoHS-compliant materials.
By aligning with these trends, you can enhance your brand's reputation and gain a competitive edge in the industry.
RoHS compliance offers significant financial benefits. It reduces the costs associated with regulatory penalties and product recalls. According to a European Commission study, non-compliance with RoHS can cost businesses up to $10 billion annually. By adhering to these regulations, you avoid such risks and save money.
Additionally, compliance streamlines manufacturing processes. A recent industry report highlights a 79.5% reduction in compliance costs and a decrease in supplier engagement time from 12 months to just 4.5 months. These efficiencies free up resources, allowing you to focus on revenue-generating activities.
| Metric | Result |
|---|---|
| Reduction in compliance costs | 79.5% |
| Supplier engagement time | 4.5 months (down from 12 months) |
| Cost savings on compliance-related expenses | 35% |
By using RoHS-compliant materials, you not only save money but also reduce operational risks, ensuring long-term business sustainability.
RoHS compliance is essential for producing safe and sustainable electronic enclosures. It encourages the use of eco-friendly materials, replacing hazardous substances like cadmium with safer alternatives. Over 60% of manufacturers now adopt recycled plastics or bio-based polymers, aligning with environmental goals. Additionally, 78% of enclosure producers require suppliers to disclose material compositions, ensuring transparency. By prioritizing RoHS standards, you protect the environment, enhance product safety, and meet consumer expectations. This commitment also strengthens your market position and reduces regulatory risks, making compliance a smart business strategy.
| Impact Area | Key Outcome |
|---|---|
| Material Selection | Safer alternatives replace hazardous substances like cadmium. |
| Recycled Materials Use | Over 60% of manufacturers adopt recycled or bio-based polymers. |
| Supply Chain Dynamics | 78% of producers demand full material disclosure from suppliers. |
RoHS compliance ensures electronic products contain reduced levels of hazardous materials. This protects users and the environment from exposure to toxic substances. It also guarantees that products meet international safety standards, making them safer and easier to recycle.
Lead-free solder eliminates the use of lead, a restricted substance under RoHS. It reduces health risks for workers and consumers while minimizing environmental contamination. Manufacturers often use alternatives like SnAgCu formulations to meet compliance requirements.
You can verify compliance by sourcing materials from certified suppliers. Testing methods like X-ray fluorescence (XRF) detect restricted substances. Proper documentation and certifications also confirm that materials meet RoHS standards.
Using non-compliant materials can lead to regulatory penalties, product recalls, and environmental harm. Toxic substances like cadmium and mercury pose risks to ecosystems and human health. Always prioritize RoHS-compliant materials to avoid these consequences.
RoHS-compliant materials may have slightly higher upfront costs. However, they reduce long-term expenses by avoiding penalties and recalls. Their durability and recyclability also lower operational costs, making them a cost-effective choice for manufacturers.